Faculty of Mathematical Informatics

Faculty introduction
Let's work together to create an AI society in which people play a leading role by learning and practicing mathematics and information.

Hiroshi Imai, Dean,
Faculty of Mathematical Informatics
Come learn about the goal of the Faculty of Mathematical Informatics, which will be born in 2024, to "create an AI society in which people play a leading role through the power of information and mathematics. Generative AI has dramatically increased the level of human-machine interaction and is just now having a widespread impact on society. In its realization, machine learning and computational methods that realize AI based on mathematics, information system machines such as quantum computers for high-speed processing, and large amounts of data via the Internet are key. In fact, these have been created from the fundamentals of information and mathematics and realized as information systems, which is exactly what you will learn in the systematic curriculum of the Faculty of Mathematical Informatics, where you will acquire practical skills through Project Based Learning and the ability to become an advanced human resource in AI, information and communication technology (advanced ICT), In society, let's create an AI society in which people play a leading role, in cooperation with our university's more than 160 years of knowledge about humans and society.
Features of Education
Mathematical comprehension
Education to develop mathematical comprehension skills to adapt to fast changes in the field of information science assembled with mathematical materials.
Social Connections
Education that gives consideration to information ethics and a strong awareness of the interface and linkage between information and mathematical sciences and society
Utilization of advanced ICT
Education in information science with a basic education in mathematical science and what can be done with computers and AI in the future.
Active in the International Community
Education that enables students to apply the advanced ICT skills they have acquired in the international community, to obtain information from the world, and to transmit it themselves.
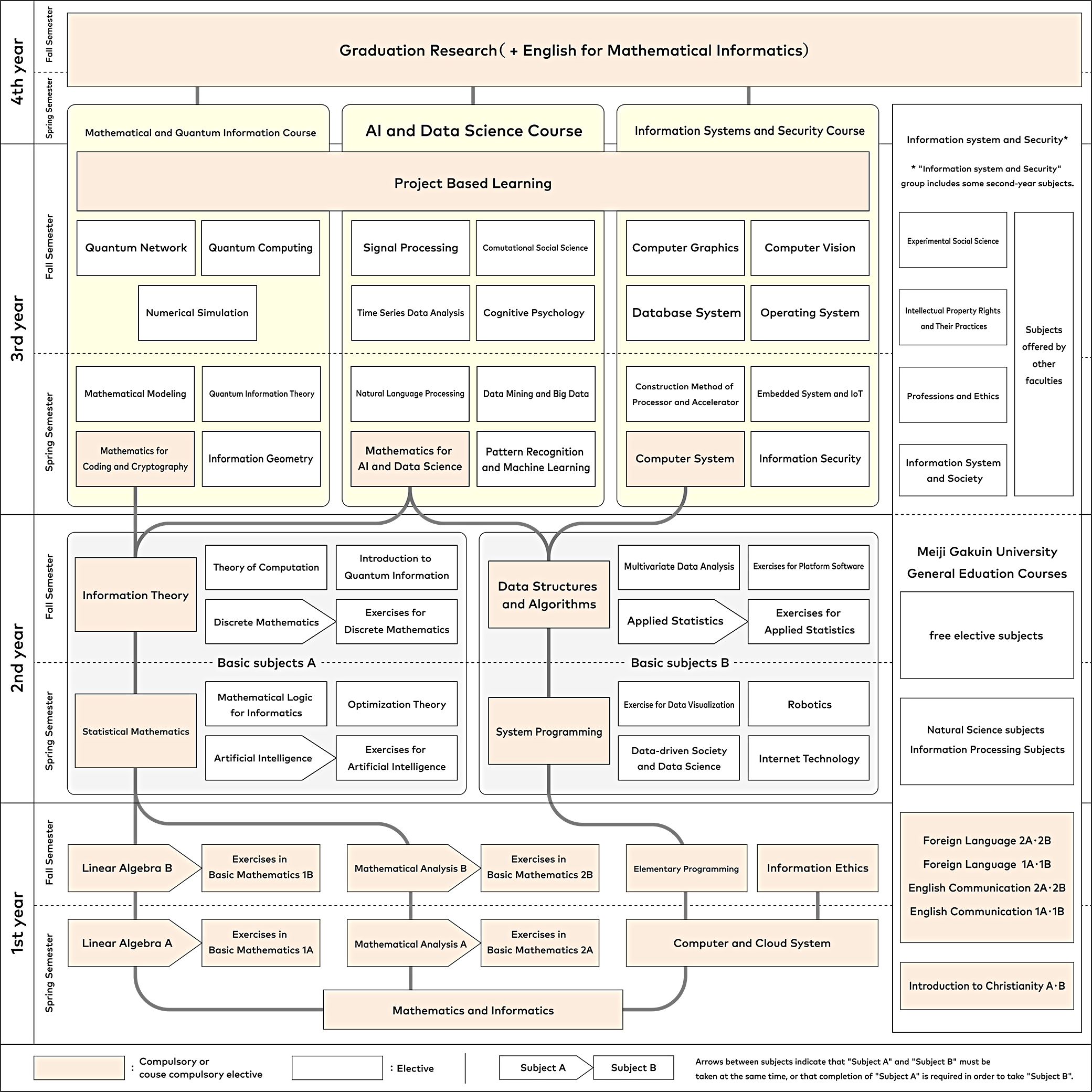
Curriculum
Courses in the third and fourth years are classified into "Mathematical and Quantum Information," "AI and Data Science," and "Information Systems and Security," allowing students to choose which field of study to focus on according to their aspirations and career path after graduation.
We provide practical education that enables students to experience the process of problem-solving Project Based Learning (PBL) in the third year, just as it is done in an actual company.
First year
- Basic Mathematics and Exercises
- information ethics
- Elementary Programming
- Meiji Gakuin Common Subjects
Featured
Mathematics and Information
The course is an omnibus lecture series featuring full-time faculty members and guest lecturers from outside the university, such as companies, to provide students with a bird's-eye view of the role of mathematics in information science and to help them choose future courses.
information ethics
In order to realize our educational philosophy of "Do for Others" through the power of information science, we will also focus on ethics education that takes into account the impact of AI on society.
Basic Mathematics and Exercises
In order to acquire the mathematical skills that will form the basis of the academic curriculum, basic mathematics education, which also takes into consideration the connection from high school, will be enhanced and thoroughly implemented in first-year education, including seminar courses.
Elementary Programming
In many of the programming-oriented lectures and exercises, students are expected to bring their own PCs to the classroom (BYOD: Bring Your Own Device) for hands-on, practical education.
2nd year
- Fundamentals A (Mathematical Informatics)
- Fundamentals B (Information Systems)
- Meiji Gakuin Common Subjects
Featured
Basic Subjects A and B
The second-year courses, including required courses, are broadly classified into mathematical and information science courses to provide a curriculum tailored to the characteristics and preferences of students, and to serve as reference for course selection in the third year.
3rd and 4th year
Mathematical and Quantum Information Course
- Mathematics of Codes and Cryptography
- information geometry
- Mathematical Modeling
- quantum computing
- Quantum networks, etc.
AI and Data Science Course
- Mathematics of AI and Data Science
- Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
- natural language processing
- cognitive psychology
- Computational Social Science, etc.
Information Systems and Security Course
- computer system
- Information Security
- Embedded Systems and IoT
- operating system
- Computer graphics, etc.
Featured
PBL (3rd year)
While providing practical education that enables students to experience processes as they are conducted in actual companies, the program also offers problem-solving exercise classes that make full use of the mathematical informatics knowledge they have acquired up to that point.
Graduation Research (4th year)
Students are assigned to a full-time faculty member's laboratory and compile research results under the guidance of the faculty member.
Society and Information (3rd year)
Courses that are conscious of the contact and fusion of information science with the humanities and social sciences, career development courses, etc. will be arranged. Courses offered by other faculties will be actively accepted, and courses will also be offered to other faculties.
curriculum tree
Anticipated post-graduation career path
Through their studies in the department, students will acquire the mathematical understanding and knowledge necessary for the utilization of advanced ICT, which will enable them to expand their fields of activity to the various occupations required in the near future, when humans and AI will coexist at a high level.
course: Mathematical and Quantum Information
To acquire the ability to apply and solve problems based on mathematical understanding, and to cultivate the ability to be involved in international research and development in cutting-edge fields such as quantum information. Students are expected to become researchers, engineers, consultants, etc. at universities and companies.
course: AI and Data Science
The program is designed to develop students' understanding and skills in AI and data science, which are the basis of advanced ICT, and to cultivate their ability to work in a wide range of occupations while integrating them with various academic fields.
course: Information Systems & Security
Cultivate the ability to utilize technologies related to information systems and information security while maintaining a mathematical understanding and high ethical standards in information science. We envision students to become programmers, system engineers, and security engineers.
Contact
Admissions Information
Admission Information
mginfo@mguad.meijigakuin.ac.jp
03-5421-5151
About the interview
Public Relations Division, Office of the President
koho@mguad.meijigakuin.ac.jp
03-5421-5165
